Introdução
Anodizing has become one of the most important surface treatments in piercing jewelry. It not only enhances visual appeal through vibrant colors but also increases corrosion resistance and durability—qualities highly valued by professionals and consumers alike. In this article, we explore how anodizing works, its application on titanium and stainless steel, and how it influences the aesthetics, biocompatibilidade, and long-term performance of piercing jewelry.
What Is Anodizing?
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that thickens the natural oxide layer on metals, como titânio e alumínio. For piercing jewelry, this process improves:
- Corrosion resistance
- Scratch durability
- Biocompatibilidade
- Color variation (in titanium)
The process involves:
- Cleaning the jewelry thoroughly
- Submerging it in an acid-based electrolyte bath
- Applying electrical current at controlled voltages
- Producing colors based on light refraction (not pigments)
👉 Related: ASTM F136 Titanium vs. 316L Stainless Steel – Which Is Best?
Anodizando de titânio: Cores, Safety & Performance
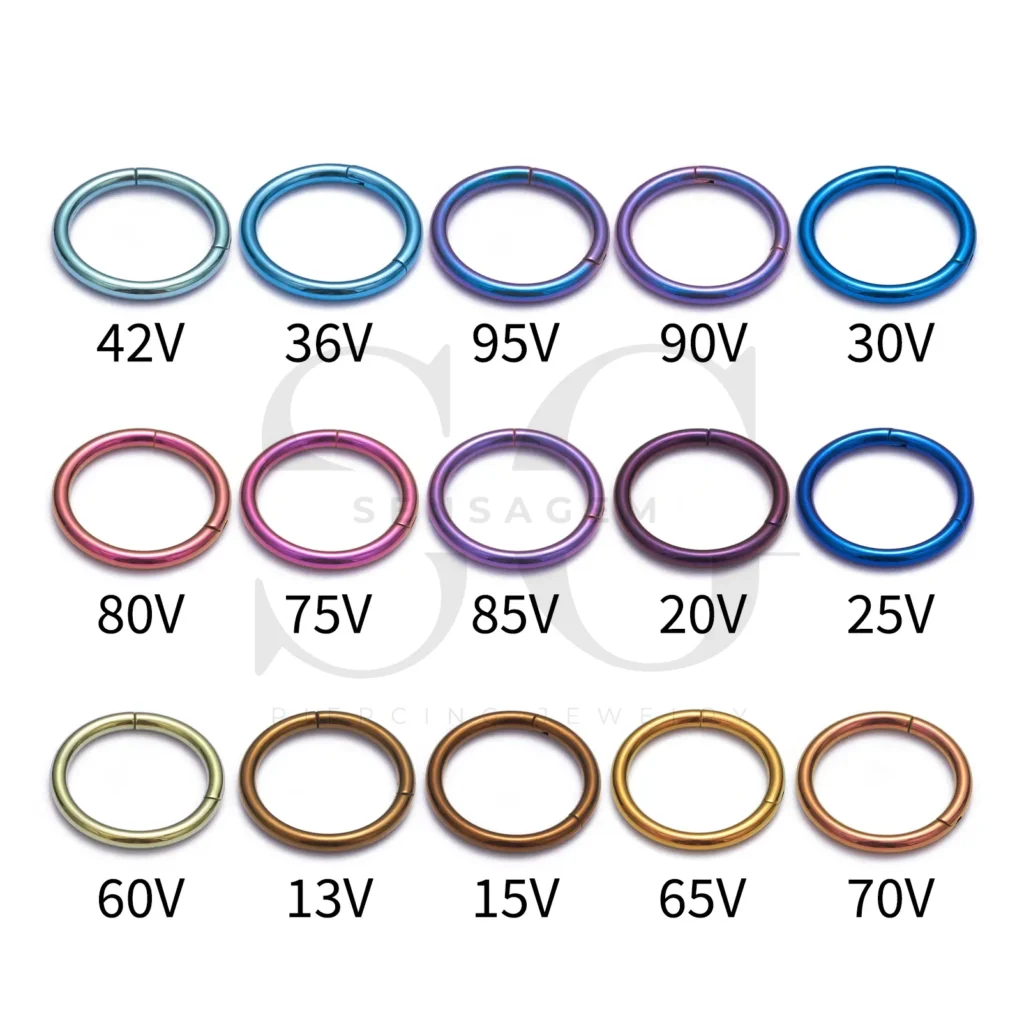

Titanium is the most suitable material for anodizing in piercing jewelry.
Advantages include:
- Wide color range: from bronze and blue to rainbow gradients
- Nickel-free e hipoalergênico, suitable for new piercings
- Improved scratch and corrosion resistance
- Customizable for branding or fashion differentiation
👉 Learn more about Piercing Jewelry Certification Standards
Process overview:
- Cleaned with acetone or alcohol
- Submerged in sulfuric acid electrolyte
- Voltage controls color outcome
- Final rinse in deionized water to seal the layer
Anodizador de aço inoxidável: Limitations & Niche Appeal
While stainless steel can be anodized, it’s far less flexible than titanium.
Drawbacks:
- Limited color palette: mostly dark tones like bronze or black
- Surface changes are subtle and less vibrant
- May still contain nickel (less hypoallergenic)
Where it works:
- Matte black or gunmetal aesthetic
- Industrial-style designs
- Cost-sensitive product lines
Steel is better suited for Revestimento em PVD ou electroplating if color is needed.
Comparando titânio vs.. Anodizador de aço inoxidável
| Recurso | Anodizando de titânio | Anodizador de aço inoxidável |
|---|---|---|
| Alcance de cores | Largo (De ouro a tons de arco -íris) | Limitado (tipicamente tons escuros ou neutros) |
| Durabilidade | Altamente resistente a arranhões e duradouros | Bom, mas um pouco menos durável que o titânio |
| Biocompatibilidade | Excelente, hipoalergênico | Bom, mas pode irritar a pele sensível |
| Custo | Mais caro | Mais acessível |
| Melhores usos | Piercings de alta visibilidade, moda, pele sensível | Estilo industrial, acabamentos sutis, econômico |
Why Anodized Jewelry Is in Demand
Piercing clients want jewelry that is:
- Visually unique
- Safe for sensitive skin
- Long-lasting under daily wear
Anodizing delivers all three—especially when applied to titanium. Studios and retailers benefit by offering bold, seguro, customizable pieces that set their brand apart.
👉 Also read: Safety Guide for Piercing Jewelry Materials
👉 Learn more in our Guia final para titânio por atacado & Stainless Steel Jewelry
Tendências & Future Outlook
- Gradient anodizing: Multi-color effects becoming popular
- Eco-friendly methods: Water-based electrolytes and closed-loop systems
- 3D-printed + anodized titanium: Custom shapes with premium finishes
Expect more studios to demand anodized titanium as consumers lean toward bold yet skin-safe jewelry.
Conclusão
Anodizing is more than decoration—it’s a functional upgrade to piercing jewelry. Titanium offers the broadest color range and safest performance for new piercings, while stainless steel offers basic anodizing for industrial aesthetics. By understanding both materials’ capabilities, you can confidently choose jewelry that meets your clients’ needs for safety, color, e durabilidade.
👉 Explore anodized titanium jewelry at Sensagem, ou Contate-nos to request samples and customization options.